Dental Radiographs
Dental radiographs (x-rays) are the images of the teeth and the oral structures that a dentist uses to evaluate oral health. These radiographs are used with low levels of radiation to capture images of the soft tissues as well as the hard tissues of the oral cavity. X-rays are used to identify the condition of teeth, roots, jaw misplacements, and facial bone abnormalities. These can even be used to identify oral lesions involving bones like tumors and other malignant abnormalities of bones. They are used to determine the depth of the cavity and the amount of bone loss which helps the dentist to properly diagnose and render appropriate treatment to the patient.
Clinical Uses
- Dental caries on the occlusal surface as well as in between the teeth
- Amount of bone destruction or bone loss
- Dental occlusal abnormalities
- Temporomandibular dislocations
- Dental or facial bone fractures
- Oral cysts and malignant or benign tumors
- Sinus abnormalities
- Helpful in dental implant surgeries
- Teeth impactions
- Periodontal or gingival abscesses
- Old or worn-out restorations to check for reinfection due to seepage
Types of dental radiographs
There are two types of dental radiographs i.e intraoral and extraoral radiographs.
Intraoral radiographs include the following
Iopa( intraoral periapical radiographs)
It shows the whole tooth structure from the crown portion to the root surface of the teeth. Periapical radiographs are used to determine the dental cavities and also detect any unusual changes in the root and the surrounding structures of the teeth.
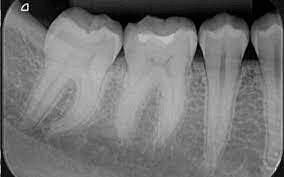
Bitewing radiographs
Bitewing radiographs show details of the crown to the level of supporting structures like the bone of both upper and lower jaws. Bitewing x-rays detect a cavity in between the teeth and are also used to check for any wear or broken dental restorations.
Occlusal radiographs
Occlusal radiographs track the development and placement of an entire arch of the teeth in either lower or upper jaws and are used for detecting the occlusal caries of the teeth.
Extraoral radiographs include the following
- Panoramic radiographs show the entire view of the mouth which includes all the teeth in both upper and lower jaws in a single x-ray. It can be used to detect dental impactions and partially erupted teeth. We can also determine the mixed dentition in the children’s x-ray. Tumors and cysts can also be detected.
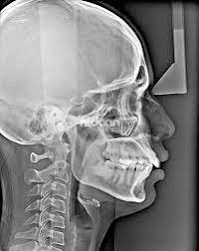
- Cephalometric radiographs are mainly used in orthodontic treatments. It shows the half side of the head in lateral view. The dentist uses this x-ray to determine the malalignment of the teeth and the jaw bones.
- Tomographs show a particular layer or a slice of the oral cavity and blur out the other layers. These are used to examine structures that are difficult to see due to blockage from the other surrounding structures.
- CBCT(Cone-beam computed tomography) is a 3D x-ray that shows the images of the soft tissues, nerves, and bone along with the teeth. Cone-beam computed tomography is widely used in diagnosing the difficult impactions involving nerves and is also used in planning for implant surgeries. It produces high-quality radiographs and dentists can determine them in 3D view. It can also be used to determine soft tissue malignancies and cysts and tumors in the oral cavity.
- Sialogram is used to detect any abnormalities in the salivary glands. It uses a dye, which is initially injected into the salivary glands to be detected and viewed on the radiograph for any malfunctioning. It can determine salivary gland blockages and also a few syndromes of the glands.
- Digital Imaging is a 2D type of digital radiograph that allows being sent directly to the computer. The images of the teeth can be seen directly on the computer screen, printed, or can be directly stored in a matter of seconds. The images can be easily transferred or easily sent to the other dentists for a second opinion. These radiographs use less radiation than the other radiographs.